Loss of hearing may be a slow and gradual process for some people. It can also be a sudden and quick loss. Hearing loss can be the result of the aging process. Often, prolonged exposure to loud noises can affect hearing. Remember, if hearing loss is caused by an affliction that can be treated, the hearing can be restored. This includes ear infections. Untreated hearing loss can be harmful, and seeking medical treatment is a good idea.
About Ear Infections
Different types of infections emerge in the ear. They can occur at any age. Usually, a child will get an infection in their ear. Kids tend to get more infections than adults do. The pus and swelling from the infection tend to prevent full hearing. A physician can inquire about the symptoms and will look at the eardrum for additional information. An otoscope is an instrument that is used to peer into the ear. The following are signs of a severe ear infection:
- Red Eardrum
- Fluid behind a bulging eardrum
- Inflammation
- A spinning sensation or dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Trouble walking or issues with balance
- Fever
- The ear may feel like it is full
- Pain in the ear
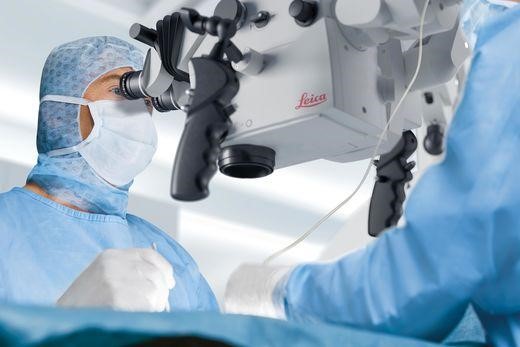
Microscopic Ear Surgery is a procedure done using a surgical microscope. The ear structure is small, so the surgical microscope helps an ENT surgeon treat the ear disease.
Visibility within the ear is poor, and surgery is delicate. We use the latest operating microscope for ear surgeries at our institute. These quality instruments aid us in providing the highest level of precision to aid our patient’s treatments.
What are the Common Symptoms of a Perforated Ear?
- Ear Pain
- Buzzing in the ear
- Decrease in Hearing or Hearing Loss
- Middle Ear Inflammation or infection, causing ear discharge.
Tympanoplasty –
Surgery is performed to repair the perforated eardrum and reconstruct the hearing mechanism.
When is Tympanoplasty needed?
Your Doctor may recommend Tympanoplasty in case of
- Ear Pain
- Buzzing in the ear
- Decrease in Hearing or Hearing Loss
- Middle Ear Inflammation or infection, causing ear discharge.
Mastoidectomy
Mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure of the temporal bone that opens postauricular air cells by removing the thin bony partitions between them. Each mastoidectomy is unique because of the variable pneumatization patterns of the temporal bone.
A mastoidectomy can treat chronic ear infections like cholesteatoma and minimize their recurrence (return). In addition, the procedure can prevent severe complications of cholesteatoma, such as:
- Hearing loss.
- Vertigo.
- Dizziness.
- Facial nerve damage.
- Labyrinthitis.
- Meningitis.
- Brain abscess.
A mastoidectomy is done using a surgical drill with the help of the microscope. all diseased bone is removed. Your doctor may suggest the type which is best suited for your condition.
- Cortical Mastoidectomy with or without Tympanoplasty and Ossiculoplasty
- Modified Radical Mastoidectomy for removing cholesteatoma
Stapes Surgery
When a disease called otosclerosis strikes the middle ear, the stapes – the smallest bone of the ear and also of our body – goes static, stops vibrating, and the sound conduction part of the hearing mechanism is disturbed, leading to hearing loss. Stapes surgery (or stapedectomy) is a microsurgery that involves the construction of an alternative sound conduction mechanism to bypass the fixed stapes to restore hearing. This is an hour-long surgery usually performed under general anesthesia, though some surgeons may prefer to operate with local anesthesia.
Conditions treated
- Hearing loss due to otosclerosis
Why this surgery?
- Stapes surgery is an elective (not a life-saving surgery) that one can choose to have. However, if opted, it will improve the quality of life by freeing one’s dependence on cumbersome hearing aids.
Benefits
Though a stapes surgery will not stop the progression of otosclerosis, it can significantly improve a person’s hearing by constructing an alternative sound conducting mechanism.

